Problem Set 3
The first two problems are trivial (while the rests are also quite trivial, well).
Need to get myself familiar with ∘.f and ⌿.
PassFail#
Write a function PassFail which takes an array of scores and returns an array of the same shape in which F corresponds to a score less than 40 and P corresponds to a score of 40 or more.
PassFail 35 40 45
FPP
PassFail 2 5⍴89 77 15 49 72 54 25 18 57 53
PPFPP
PFFPPSolution#
PassFail←{'PF'[1+⍵<40]}Grille#
This problem is taken from the 2019 APL Problem Solving Competition.
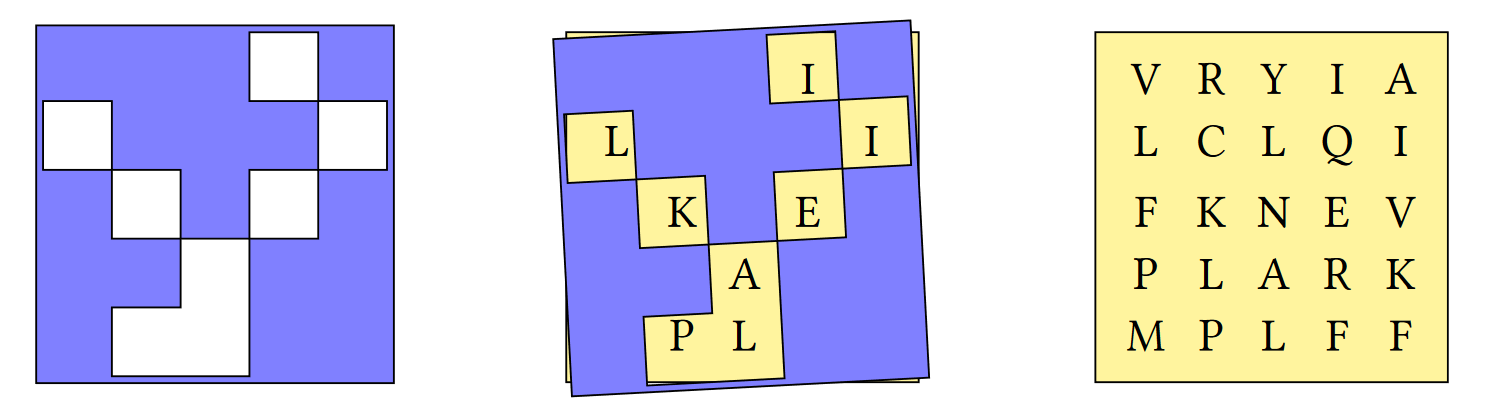
A Grille is a square sheet with holes cut out of it which, when laid on top of a similarly-sized character matrix, reveals a hidden message.
Write an APL function Grille which:
- takes a character matrix left argument where a hash
'#'represents opaque material and a space' 'represents a hole. - takes a character matrix of the same shape as right argument
- returns the hidden message as a character vector
(2 2⍴'# # ') Grille 2 2⍴'LHOI'
HI
grid ← 5 5⍴'VRYIALCLQIFKNEVPLARKMPLFF'
grille ← 5 5⍴'⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺ ⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺⌺ ⌺⌺'
grid grille
┌─────┬─────┐
│VRYIA│⌺⌺⌺ ⌺│
│LCLQI│ ⌺⌺⌺ │
│FKNEV│⌺ ⌺ ⌺│
│PLARK│⌺⌺ ⌺⌺│
│MPLFF│⌺ ⌺⌺│
└─────┴─────┘
grille Grille grid
ILIKEAPLSolution#
Though lengthy in fact really simple:
Grille←{⍵[⍸⍺=' ']}Back to School#
Write a function to produce the multiplication table from
1to⍵.MulTable 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 7 14 21 28 35 42 49Write a function to produce the addition table from
0to⍵.AddTable 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Solution#
MulTable←{a∘.×a←⍳⍵}
AddTable←{a∘.+a←¯1+⍳⍵+1}Making the Grade#
| Score Range | 0-64 | 65-69 | 70-79 | 80-89 | 90-100 |
| Letter Grade | F | D | C | B | A |
Write a function that, given an array of integer test scores in the inclusive range 0 to 100, returns a list of letter grades according to the table above.
Grade 0 10 75 78 85
FFCCBSolution#
Grade←{'FDCBA'[1+ +⌿65 70 80 90 100∘.≤⍵]} Analyzing text#
Write a function test if there are any vowels
'aeiou'in text vector⍵AnyVowels 'this text is made of characters' 1 AnyVowels 'bgxkz' 0Write a function to count the number of vowels in its character vector argument
⍵CountVowels 'this text is made of characters' 9CountVowels 'we have twelve vowels in this sentence' 12Write a function to remove the vowels from its argument
RemoveVowels 'this text is made of characters' ths txt s md f chrctrs
Solution#
The first one is easy:
AnyVowels←{∨/,'aeiou'∘.=⍵}Same with the second one:
CountVowels←{+/,'aeiou'∘.=⍵}The official solution to the third question is obviously wrong. Correct one:
RemoveChars←{⍵[⍸∧⌿~⍺∘.=⍵]} ⍝ version 1 using index
RemoveCharsAlt←{⍵/⍨∧⌿~⍺∘.=⍵} ⍝ version 2 using replicateso that 'aeiou' RemoveChars ‘this text is made of characters’. Unfortunately this doesn't work when there is only one character as ⍺, namely 'a' RemoveChars ‘abc’ won't work as intended. This is because ⌿ works just like / for rank 1 vectors (the first axis is the same as the last axis):
+⌿ 1 2 3
6In Dyalog we have guards, hence:
RemoveChars←{2<⍴⍺,1:⍵/⍨∧⌿~⍺∘.=⍵⋄2=⍴⍺,1:⍵/⍨~⍺∘.=⍵} ⍝ a hack
RemoveChars←{t←⍴⍴⍺⋄1=t:⍵/⍨∧⌿~⍺∘.=⍵⋄0=t:⍵/⍨~⍺∘.=⍵} ⍝ betterIn fact the true APL way of handling this is ~⍨:
'a' ~⍨ 'this text is made of characters'
this text is mde of chrcters
'aeiou' ~⍨ 'this text is made of characters'
ths txt s md f chrctrsMatching Shapes#
Solution#
AddRows←{⍺+(⍴⍺)⍴⍵}
AddRows←{m←(⍴⍺)⌈⍴⍵⋄(m⍴⍺)+m⍴⍵}Matching elements#
Solution#
h←⌈/height
m←height=⌈/height
h
m⌿student
m/class
m←(class='B')/height⋄+/m÷≢mOptimus Prime#
Solution#
Primes←{s←⍳⍵⋄q←{2=+/0=s|⍵}⋄s⌿⍨q¨s}The original one is definitely better, while still not good in terms of algorithm:
Primes←{⍸2=+⌿0=∘.|⍨⍳⍵}